34 funding and performance of R&D in France and by businesses
This page has been updated. Read 34. funding and performance of R&D in France in Higher education & research in France, facts and figures 10th edition - June 2017
Businesses provide the majority (60%) of funding for gross national expenditure on R&D, with businesses based in France financing around 55% of the country’s gross domestic expenditure on R&D. This level of funding by the private sector is much lower than that recorded in Japan, Germany and the United States.
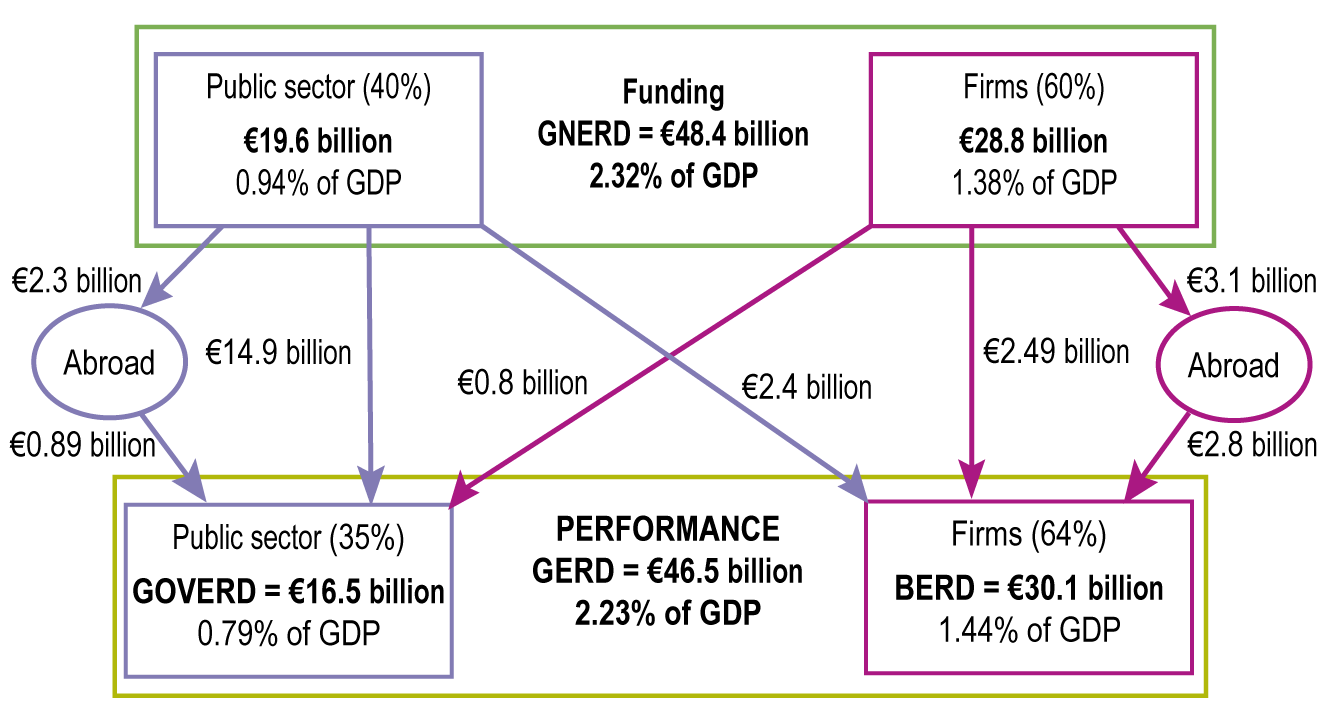
In 2012, businesses and the public sector provided €48.4 billion in funding for R&D performed either in France or abroad. Businesses funded 60% and the public sector 40% of the country’s gross national expenditure on R&D (GNERD) (diagram 34.01).
In parallel, gross domestic expenditure on R&D (GERD), which covers all R&D performed within France, totalled €46.5 billion in 2012, €30.1 billion of which was implemented by businesses (intramural business enterprise expenditure on R&D – BERD) and €16.5 billion by the government (intramural government expenditure on R&D – GOVERD). GERD was financed through cross-investment by French businesses (55%), the French government (37%) and funding from abroad (8%). The level of funding by the private sector was much lower than that recorded in Japan (76%), South Korea (75%), Germany (66%) and the United States (59%) (chart 34.02). In the United Kingdom, although businesses funded less than half of GERD (46%), 20% of R&D funding came from abroad, as compared with only 8% in France.
Total business enterprise expenditure on R&D (see ‘Methodology’ section opposite) amounted to €33.7 billion in 2012. Self-financing of €24 billion and inter-business funding streams worth €6.8 billion together financed more than 90% of this expenditure in 2012 (chart 34.03a). Funding streams from businesses within the same group accounted for €5.6 billion of these €6.8 billion, while those between businesses belonging to different groups represented only €1.1 billion (chart 34.03b). International organisations, the European Union and above all funding from the French government accounted for the remaining funding for R&D expenditure by businesses (€0.5 billion and €2.5 billion respectively) (chart 34.03a).
Government funding for R&D by businesses is understood to mean R&D contracts signed with dedicated state research institutions, as well as support measures provided by the state, whether direct or indirect. ‘Direct’ support is provided by means of subsidies, calls for proposals and contracts supporting programmes that tackle key issues. ‘Indirect’ government support takes the form of different tax incentives and repayable (where projects result in commercial success) advances, which are not included in this analysis. The most significant form of tax relief is the R&D tax credit (crédit d’impôt recherche – CIR), with a total of €5.3 billion paid out to 15,300 businesses based in France in 2012.
Due to the importance of military R&D programmes, 48% of government funding for R&D contracts signed with businesses came from the French Ministry of Defence. Such funding therefore remained highly concentrated within a small number of research areas. Four branches of activity received almost half of government funding: ‘manufacture of air and spacecraft and related machinery’ (28%); ‘manufacture of communication equipment’ (10%); ‘manufacture of fabricated metal products, except machinery and equipment’ (9%); and ‘manufacture of instruments and appliances for measuring, testing and navigation; watches and clocks’ (9%).
Insee
MENESR-DGESIP/DGRI-SIES.
How to cite this paper :
close
Key figures
Whole of France
Whole of France
Whole of France
Whole of France
Whole of France
Whole of France
Whole of France
34.01 Funding and performance of research and development in France in 2012
Insee
You can embed this diagram to your website or your blog by copying the HTML code and pasting it into the source code of your website / blog:
close
34.02 Proportion of GERD funded by businesses, the public sector and from abroad in 2012 in the major OECD countries (%)
1 Government, higher education and the private non-profit sector.
2 Including international organisations.
3 2011 data.
4 Excluding capital expenditure, funding from abroad is included in the other categories.
You can embed this chart to your website or your blog by copying the HTML code and pasting it into the source code of your website / blog:
close
34.03a Sources of funding for total business enterprise expenditure on R&D in 2012 (in €bn) 1
1 'total business enterprise expenditure on R&D' corresponds to the sum of funding for intramural business enterprise expenditure on R&D and that for business enterprise expenditure on R&D implemented in the public sector and abroad.
You can embed this chart to your website or your blog by copying the HTML code and pasting it into the source code of your website / blog:
close
34.03b Funding for business enterprise R&D provided by third party businesses in 2012 (in €bn) 1
1 'total business enterprise expenditure on R&D' corresponds to the sum of funding for intramural business enterprise expenditure on R&D and that for business enterprise expenditure on R&D implemented within the public sector and abroad.
You can embed this chart to your website or your blog by copying the HTML code and pasting it into the source code of your website / blog:
close
34.04 Government funding for military and civil R&D programmes carried out by businesses in 2012 (%)
You can embed this chart to your website or your blog by copying the HTML code and pasting it into the source code of your website / blog:
close
Related statistical publications
 Note recherche 06.02 - L'externalisation de la R&D : quel arbitrage entre sous-traitance et coopération ? - Estelle Dhont-Peltrault, Etienne Pfister - March 2006
Note recherche 06.02 - L'externalisation de la R&D : quel arbitrage entre sous-traitance et coopération ? - Estelle Dhont-Peltrault, Etienne Pfister - March 2006 
 Note recherche 05.01 - Les relations interentreprises en R&D - Estelle Dhont-Peltrault - May 2005
Note recherche 05.01 - Les relations interentreprises en R&D - Estelle Dhont-Peltrault - May 2005 Translation
 Etat de l'enseignement supérieur et de la rechercheL'état de l'Enseignement supérieur et de la Recherche en France n°8 - juin 2015
Etat de l'enseignement supérieur et de la rechercheL'état de l'Enseignement supérieur et de la Recherche en France n°8 - juin 201534 - le financement et l'exécution de la R&D en France et dans les entreprises - Catherine David






